Loading
-
691.
-
692.
-
693.
-
694.
-
695.
Statement for Linked Answer Questions:
Consider a baseband binary PAM receiver shown below. The additive channel noise n(t) is whit with power spectral density SN(f)=N0/2=10-20 W/Hz. The low-pass filter is ideal with unity gain and cutoff frequency 1MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
Yk=Nk if transmitted bit bk=0
Yk=a+Nk if transmitted bit bk=1
Where Nk represents the noise sample value. The noise sample has a probability density function, PNk(n)=0.5αe-α|n| (This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2=10-6V.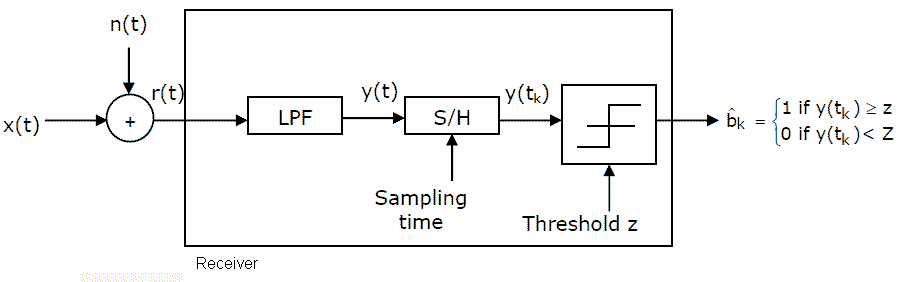
[1] The value of the parameter α (in V-1) is [2 marks]
(A) 1010
(B) 107
(C) 1.414x10-10
(D) 2x10-20[2] The probability of bit error is [2 marks]
(A) 0.5xe-3.5
(B) 0.5xe-5
(C) 0.5xe-7
(D) 0.5xe-10asked in Electronics and Communication Engineering, 2010
View Comments [0 Reply]
-
696.
Statement for Linked Answer Questions::
The silicon sample with unit cross-sectional area shown below is in thermal equilibrium. The following information is given: T=300K, electronic charge=1.6x10-19C, thermal voltage=26mV and electron mobility = 1350cm2/V-s
[1] The magnitude of the electric field at x=0.5 μm is [2 mark]
(A) 1kV/cm
(B) 5kV/cm
(C) 10 kV/cm
(D) 26kV/cm[2] The magnitude of the electron drift current density at x=0.5 μm is [2 marks]
(A) 2.16x104 A/cm2
(B) 1.08x104 A/cm2
(C) 4.32x103 A/cm2
(D) 6.48x102 A/cm2asked in Electronics and Communication Engineering, 2010
View Comments [0 Reply]
